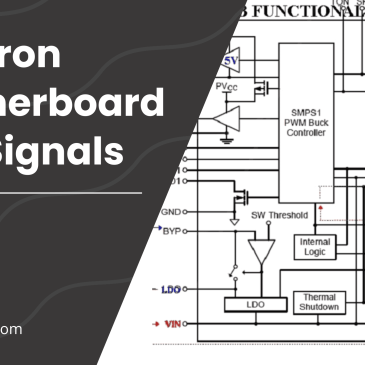
Free schematics bios boardviews
Schematics Bios Boardviews for all latest and old laptops and desktops. Which brand’s schematics are available We offer brands like Hp Dell Lenovo Samsung Apple Asus Acer Sony Msi Avita Hcl Toshiba laptops and desktop schematics bios and boardview free … Continued