Understanding the power sequence of laptop motherboards is very important. Firstly the power sequence is the exchange of voltages and signals between the motherboard chips.
Secondly, This happens before anything appears on the screen.
The power sequence is the phase in which the motherboard prepares itself to function. This phase consists of sending orders to different voltage generators from some ICs. Secondly, receiving confirmation makes sure the principal Integrated circuits of the motherboard are functional.
The power sequence should take place in a specific order. Secondly, if one signal or confirmation is not sent or received then this phase stops there and finally, nothing will work.
The power sequence is used to troubleshoot laptop motherboard problems by testing voltages because the absence of some voltages indicates problems with some ICs. Also in some schematics, the power sequence is described which makes troubleshooting easier.
Steps To Check Voltage And Signal Sequence For Laptop Motherboard Power On Stage
The steps are known as ladders for voltages and signals. These steps are given below.
ALWAYS VOLTAGE Checking
This voltage generates before the power on the button is pressed. 3Volt is given to SIO and EC BIOS.
After Pressing The POWER BUTTON
Once the power button presses SIO to inform PCH and turn buck converters one after another.
POWER ON VOLTAGES check
The voltage after power should be produced as given below :
- 3.3 Volt
- 5 Volt
- 1.8 Volt
- 1.5 Volt
- 1.05 Volt
- CPU CORE
- 0.9 GFX Core
POWER GOOD Signal Check
PCH receives SYS PWR OK signal confirmation signal saying all power is ok.
RESET Signal Check
PCH generates a PLTRST signal to clear motherboard junk values and reset the motherboard.
CLOCK SIgnal Check
CLOCK starts generating different frequencies according to the requirement of chips.
Starts Reading BIOS
In this step, the CPU starts reading BIOS.
POST Checking By Motherboard
In this step motherboard test all chips and devices in this process which is also called ‘Power on self test.’
Motherboard power states for understanding laptop motherboard power on sequence stages
These are the states of the laptop depending on the power consumption of the motherboard, you already know the two states which are :
- You turn on the Laptop.
- The laptop gets turned off by you.
The motherboard states are referred to in character ‘S…’ Where the x is a number between 0 and 5.
S0 State Of Laptop Motherboard
Working, the system is fully usable, all the components have their voltage.
S1, S2, S3 State Of Laptop Motherboard
Sleep, The laptop appears to be off, the laptop consumes less power than in S0 state, the RAM has its voltage, and is kept refreshed.
To wake the laptop from this Sleep state you need only to press a key on the keyboard or move the mouse.
S4 State Of Laptop Motherboard
Hibernate, the system appears to be off, and the power consumption is reduced to the lowest level. An image of the RAM is kept on the disc because RAM loses its voltages, to wake the laptop you need to press the power button.
S5 State Of Laptop Motherboard
In this step, the laptop motherboard gets shut down.
Types Of Motherboard Voltages For Power On Sequence Stages
There are four stages in the laptop motherboard which are given below:
Always Supply Voltage Type (ALWS or AUX or AL)
These voltages are always present even when the laptop is off, on one condition: the battery should be placed or the charger plugged in. Thises voltages are:
- 5 Volt DC
- 3.3 Volt DC
The 5 Volt and 3.3 Volt come from Voltage generator ICs in the motherboard.
Suspension Voltage Type (SUS ON)
These voltages are present in suspended or sleep mode (S1, S2, S3):
- 5 Volt DC
- 3.3 Volt DC
- RAM voltage (For DDR1 – 2.5 Volt, For DDR2 – 1.8 Volt, For DDR3 – 1.5 Volt, For DDR4 – 1.2 Volt)
Note that the 5 Volt and 3.3 Volt are not the same % Volt and 3.3 Volt is Always voltage, there is another voltage generator that generates those 5 volts and 3.3 Volt.
Power On Voltage Type (RUN) (S0 State)
All the components have now their voltages. There is a supply of 1.05 Volt and 1.8 Volt is also done.
CPU Core Voltage Type
CPU requires core voltage, for example, a high current of approximately 20 Amp to 30 Amp. The newer motherboard graphics chip is also integrated into the CPU. So the graphics Core voltage is also required. These voltages are GFX core voltages. These voltages are approximate:
CPU Core = 0.8 Volt to 1.5 Volt / 20 Ampere to 30 Ampere.
GFX Core = 0.8 Volt to 1.5 Volt / 10 Ampere to 20 Ampere.
Laptop Motherboard Power Plane
There are two power input sources in a laptop motherboard one is adapter input and another is battery input.
The adapter input and battery charging section are called VIN ( Voltage Injection) sections. This section decides which power needs to be sent inside. This section has another task called battery charging. there are a number of buck convertors used according to fulfill the requirement.
Laptop Mother Powe Plane To Understanding Laptop Motherboard Power On Sequence Stages
| Voltages | Voltage Type |
|---|---|
| 3.3 Volt | Comes As Always Voltage |
| 5 Volt | This Also Always Voltage |
| 3.3 Volt | Suspended Voltage |
| 5 Volt | This Also Suspended Voltage |
| 1.5 Volt | System Run Voltage |
| 1.8 Volt | This Also System Run Voltage |
| 1.05 Volt | System Run Voltage |
| 0.75 Volt | This is Also a System Run Voltage |
| GFX Core | Graphics Core Voltage |
| CPU Core | CPU Core Voltage |
Knowing the motherboard model number is important to find the laptop motherboard power sequence. Especially when we try to find out the Laptop Motherboard Power Sequences.
It helps to find pictures, schematics, board views, and known issues. There is always a number written on the board itself. In some cases, there’s also a sticker that tells a variant.
Common Laptop Motherboard Manufacturers For Laptop Motherboard Power On Signals
Below are some of the common laptop motherboard manufacturers
Quanta
Quanta motherboard found is HP, Dell, Acer, Toshiba, and a few Lenovo laptops. The model number on the board is “DA0xxxxMByyy” (first 0 is optional), “xxxxx” is the actual model, and “yyy” contains the revision. For example DAY11AMB6E0 for Quanta Y11A rev E.
Compal
Compal motherboard found in HP, Dell, Acer, Toshiba, Lenovo. Secondly, the model number is “LA-xxxxP” (P is optional), the older, the lower the number is like LA-4082P from 2007 or LA-E541P.
LCFC
Found in Lenovo, it’s actually Compal. The model number is “NM-xxxx”.
Wistron
Found in Acer, Dell, HP, Lenovo. The model number is an “xxxx-x” (x being a digit), often associated with a name. For example “Ricjie MB 11241-1”.
Inventec
They make Toshiba, HP, and Some Acer motherboards. Secondly, their model is number is often “xxyyzz” with “x” being a letter, “y” a digit, and “z” as the optional letter.
There is also a “6050xxxxxxxx-MB-xx” number that can be easier to spot. For example “SA10E” and “6050A2052401-MB-A04” for Inventec.
Foxconn
Foxconn motherboards are found in Sony, Some HP laptops. HP has a weird model number like “CHICAGO_HR_HPCMV_MB_V1” or “PM_I_HPC_S_MV_MB_V3”.
Sony comes with an “MBX-xxxx” number that’s easy to identify, and other numbers, like “MBX-202” and “M790”.
Pegatron
Pegatron motherboards are found in a few Acer and Toshiba motherboards. Acer, in general, has an “xxyyzz” with “x” being a letter, “y” a digit, and “z” an optional letter. Toshiba has a weird model number like “PLF/PLR/CSF/CSRUMA”.
Whereas the following manufacturers make their own boards (except maybe a few models here and there):
Apple
Apple board model number is “820-xxxxx”, like “820-3462”. It’s written black on a black surface so it’s hard to spot.
Asus
Asus board model number follows the same format as the laptop model number. Secondly, It can be the same or similar, and sometimes different.
MSI
MSI model number is “MS-xxyxz”, with x being digits, y a digit or letter, and z an optional digit for revision. Some boards have two different model numbers like “MS-16J5” and “MS-1795” (with a 1 appended for the revision.
Samsung
Samsung model number is the name associated with a “BA41-xxxxxx” number, like “Bremen-D” and “BA41-01197A”.
Clevo
Clevo manufactures laptops for a lot of “small local” brands. There are two model numbers on the board, “6-71-W25S0-D02” and “W251ESMB-D0”.
HanStar doesn’t Design motherboards so we did not put them on the list. But rather HanStar manufactures the PCB. “J MV-4” and “94-V0” do not board model numbers, they are generic markings about PCB characteristics.
List Of Laptop Motherboard Power On Signals
The following are laptop motherboard power on signals:
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3 Volt power to SIO and BIOS |
| ECRST | RESET to SIO |
| LID SWITCH THERMTRIP |
The lid sensor should work The thermal trip should normal |
| Clock SIO | 32.7khz clock from either PCH |
| EC BIOS | EC BIOS should perfect |
| RTCRST | RTC RESET and crystal 32khz should to PCH |
| VCCDSW3_3 | Power to PCH |
| DPWROK | Power OK Indication for the VccDSW3_3 voltage rail |
| PWRBTN (NBSON) | Power switch 3 – 0 – 3 variation |
| RSMRST | SIO generates 3 Volt at this pin |
| PM_PWRBTN (DNBSWON) | Post power button to PCH 3 Volt variation. |
| SLP_4 SLP_3 |
PCH generates 3 Volts send to SIO giving confirmation to turn on the power |
| SYSON, SUSP, VR ON | All buck converters turn on one by one |
Signal Name And Description For Laptop Power On Signals
When power is connected either from the adapter or battery to the motherboard it passes from various stages.
Below mention a chart given signal name and their description.
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| VIN voltage | Check the input voltage to this current sensing resistor |
| VIN | VIN is 3 Volt and 5 Volt section input voltage to 3 Volt and 5 Volt chip |
| VREG3 | 3 Volt linear output from 3 Volt and 5 Volt section which is going to SIO |
| VCC | SIO gets 3 Volt at its power input pin |
| ECRST | EC reset signal 3 Volt reset to SIO |
| THERMTRIP | THERMTRIP thermal signal |
| LID SW | LID SW is a magnetic lid sensor |
| BIOS | EC BIOS starts communicating with SIO |
| NBSWRON /PWRBTN | The power switch when we press 3 Volt goes zero and then again comes to 3 Volt. Moreover, you can see their 3 Volt variation. |
| ECON | SIO generates an ECON signal and turns on always section 3.3 Volt and 5 Volt buck converter output. |
| 3.3 Volt ALW, 5 Volt ALW |
3.3 Volt and 5 Volt Buck converter output voltage. |
| PCH_PWR EN | SIO generates this signal and provides power to PCH |
| VCCDSW3.3 | PCH power management section gets 3 Volt power |
| DPWROK | This signal is confirmation to PCH power 3 Volt |
| RTCRST | RTC reset signal 3 Volt |
| SUSCLK | 32.7KHZ clock frequency to SIO |
| RSMRST | SIO sends a 3 Volt signal to PCH to reset and resume called RSMRST |
| DNBWORON PMBTN |
SIO sends post power button signal to PCH 3 Volt to zero and back |
| SLP_S4 (SUSB) | 3 Volt power plane wake up signal to PCH to reset and resume called RSMRST |
| SPL_S3 (SUSC) | 3 Volt power plan wake up signal from PCH to SIO |
| SYSON, SUSP, VR ON |
SIO turn on all buck converter one by one |
Power On Sequence Diagram For Laptop Power On Signals
Below are the diagrams for laptop power on signals.
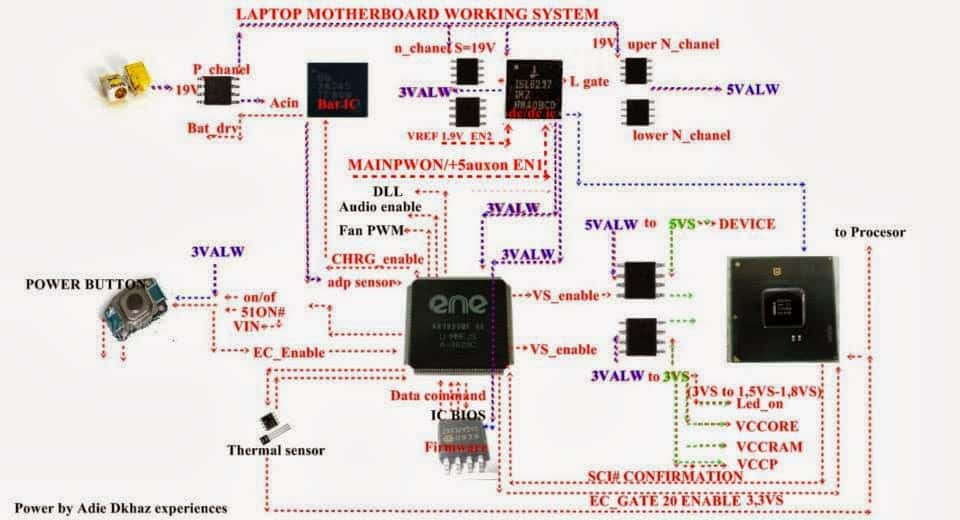
Laptop Power On Signals For General Motherboards
Below is the power on signals for general Motherboards.
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| CURRENT SENSING RESISTOR | Check here 18 Volt. Secondly, if not coming then check 1st or 2nd MOSFET or battery charging chip |
| VIN | DC Voltage input to always voltage chips at its VIN pin |
| VREG3 | 3 Volt linear output from the chip |
| VCC | 3 Volt power to SIO and BIOS |
| ECRST | 3 Volt reset signal to SIO |
| AC OK | 3 Volt signal coming from battery charging chip indicating power coming from adapter. |
| SIO start communicating with BIOS | |
| NBSWRON | The power switch goes zero and comes back to 3 Volt |
| S5_ENABLE | After the power button is pressed SIO generates an S5_ENABLE signal to 3 Volt and turns on the 3 and 5 Volt section |
| VCCDSW3_3 | This 3 Volt power turn on PCH |
| DPWROK | Power ok to PCH 3 Volt |
| SUSCLK | 32.7KHZ clock frequency coming from PCH to SIO |
| RSMRST | Resume Reset Signal |
| DNBWRON PM_PWRON |
Post power button signal generate from SIO to PCH |
| SLP_3 SLP_4 |
Wake up signal generated by PCH send to SIO |
| SUS ON SYSON |
Buck converter on signal |
Laptop Power On Signals For Quanta Motherboards
Below is the power on signals for Quanta Motherboards.
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| 3.3 VAL | 3 volt linear goes to SIO VCC pin |
| PWRBTN NBSWON | power button |
| SLP_S5 | when power press SIO sends SLP_S5 signal to enable 3 Volt and 5 Volt supply |
| 5 Volt | 5 Volt buck converter output |
| 3.3 Volt | 3.3 Volt buck converter output |
| RSMRST | SIO sends 3 signal PCH |
| PM_PWRBTN | post power button from SIO to PCH goes low and back high |
| SUSC, SLP_S4, _S3 | wake up signal sent by PCH to SIO to turn on the laptop |
| SUS ON | This signal release 3 Volt and 5 Volt |
| 5 Volt SUS | |
| SYSON | system on signal turn on the buck converter |
| 1.5 Volt (DDR3) | |
| MAIN ON | main on signal turn on 1.05 Volt and 1.8 Volt |
| 1.05 Volt, 1.8 Volt | 1.05 Volt and 1.8 Volt |
| HWPG | when all power ok then the HWPG signal generates 3 Volt and is given to SIO |
| VR_ON | once SIO receives the HWPG signal is generated a signal to the VRM section |
| VCC / GFX CORE | CPU core and GFX core voltage generated and given to CPU |
| IMVP PWRGD | when CPU core voltage stable VRM chip sends this power good signal |
| ECPWORKS (SYS PWR OK) | When all powers is ok including CPU SIO generates this 3 Volt signal to PCH |
| DRAM PWRGD | ram power ok signal |
| PLTRST | |
| CS READ | PCH read BIOS |
Laptop Power On Signals For Quanta 4th Generation Motherboards
Below is the power on signals for Quanta 4th generation Motherboards.
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| POWER | power input from the adapter and battery charging section. This voltage is approximately the adapter input voltage. |
| 3.3 VAL | this is 3 Volt linear output from the Always Voltage Section. This power goes to the SIO VCC pin. |
| PWRBTN (NBSWON) | this is the power button. It is normally 3 Volt when we press a power button it goes to 0 and comes back to 3. |
| SLP_S5 | this signal is sent by SIO to turn on Always voltage after the power button is pressed. |
| 5 Volt | 5 Volt and 3 Volt are always voltage. |
| 3.3 Volt TO PCH | this voltage to going to CPU to turn on its power. It is called VCC DSW. |
| RSMRST | This is a 3 Volt resume signal generated by SIO to resume further sequence. |
| PM_PWRBTN | This is a post power button from SIO to CPU. |
| SUSN, SLP_S3 | Wake up the signal from the CPU to turn on different Buck converters. |
| SUS ON | Suspend voltage turn on. |
| 5 Volt SUS | This is the 5 Volt and 3 Volt suspend output. |
| 1.35 Volt (DDR3) | 1.35 Volt buck convertor turned on. |
| MAINON | Turn on the main power from SIO to the buck converter. |
| 1.05 Volt | 1.05 Volt buck converter turn on. |
| HWPG | All power good signal when all the buck converter is working then HWPG signal is generated. |
| VR_ON | CPU core voltage turn ON signal. |
| VCC_CORE | CPU core voltage. |
| IMVP_PWRGD | CPU core voltage ok. |
| DGPU_PWR_EN | Graphics core voltage power good. This gives enables the signal to a 1.5 Volt buck converter. |
| GFXCORE | Graphics core voltage. |
| DGPU_VC_EN | Graphics core voltage power good. This gives Enable signal to a 1.5 Volt buck converter. |
| 1.5 Volt | 1.5 Volt buck converter voltage output. |
| DGPU_PWROK | Power ok signal to SIO. |
| EC_PWROK | All the power plans are ok including the CPU core, SIO generates this signal, even to the CPU. |
| SYS_PWROK | All system powers are working fine. |
| PLTRST | Platform reset. CPU generates the platform reset to reset the entire motherboard after it receives the system power ok signal. |
| DRAM RST PIN NO 30 | Reset signal to the RAM. |
Laptop Power On Signals For Wistron Motherboards
Below is the power on signals for Wistron Motherboards.
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| VREG 3 Volt | 3 volt linear output from always section going to SIO power |
| S5 ENABLE | from SIO to always section buck converter enable pin |
| VCCDSW | this is the power to PCH 3 Volt |
| RTC CLK | RTC section generates 32.7khz clock frequency after RTCRST signal |
| RSMRST | resume and reset 3 Volt signal generated by SIO to PCH |
| PM_PWRBTN | post power button signal generate by SIO 3 Volt variation going to PCH |
| SLP_S4 | SLP_S4 signal is wake up signal sent by PCH to SIO. |
| SLP_S3 | SLP_S3 signal is wake up signal sent by PCH to SIO. |
| 1.8 Volt | 1.8 Volt buck convertor turn on. |
| RUNPWRK | after generating 1.8 Volt this buck converter generates power good |
| 1.05 Volt | RUNPWROK power good signal goes to 1.05 Volt buck converter. |
| VTTPWRGD | when 1.05 Volt out then it generates power good and it goes enable to 0.85 VTT enable. |
| 0.85 Volt | 0.85 Volt buck converter turns on. |
| IMVP_VR_ON | CPU core enables signal. |
| VCORE | CPU core voltage output. |
| SYS_PWROK | IMVP PWRGD signal generates after CPU core voltage stable and this signal goes to PCH. This signal sends all power ok called SYS_PWROK |
| DRAMPWRGD | RAM power ok. |
| CPUPWRGD | CPU power ok. |
| PLTRST | platform reset generated by PCH and reset entire motherboard. |
Laptop Power On Signals For WISTRON 5th Generation Motherboards
Below is the power on signals for Wistron 5th generation Motherboards.
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| ACIN | adapter voltage input |
| VREG 3 Volt | 3 Volt linear output from always 3 Volt and chip |
| S5_EN | SIO sends this signal to enable 3 Volt and 5 Volt section |
| 3 Volt and 5 Volt ALW | buck converter output |
| RSMRST | SIO sends resume signal to CPU |
| ON OFF SWITCH | power button |
| PM PWRBTN | post power button from SIO to CPU |
| SLP_S3 | CPU generates this signal to turn on all buck converters. |
| 1.35 Volt | DDR3 supply turns on. |
| 1.05 Volt / 1.5 Volt | 1.05 Volt and 1.5 Volt buck converter turns on. |
| RUNPWROK | power good signal |
| H_VCCST_PWRGD | all power good signal |
| CPU CORE | CPU CORE voltage |
| IMVP_PWRGD | CPU power good signal output from VRM section |
| DRAMRST | reset signal to DDR |
| BIOS | CPU reads BIOS |
For making a career in laptop chip level repair you must have knowledge about basic Chip Level components too.
There is also a guide for desktop motherboard power sequence which is similar but much smaller compared to laptop motherboards.
